History of Space Exploration: First Rocket in the Space to First Man on the Moon
© Mahavir Sanglikar
This is a brief introduction to the major events in the history of space exploration, starting from first vehicle entering into space to first landing on the Moon.
Let us see what was achieved in which year by scientists in the history of Space Exploration. I have included only major events, and that too after the first man-made object entered in the space. I have excluded the achievements, discoveries and new findings in labs on the earth, and have included the actual entries in space.
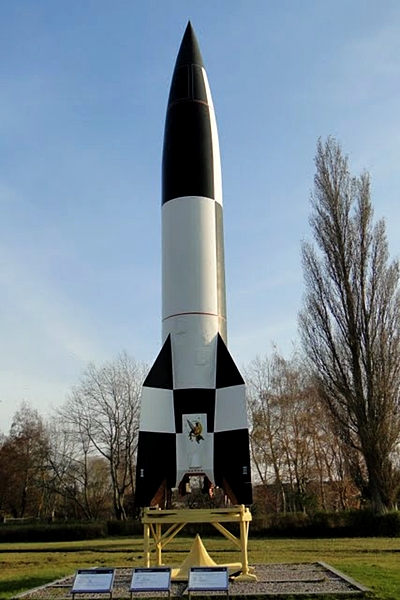

Nazi Germany Rocket Enters Outer Space: 3rd October 1942
Space starts from 100 Kilo Meters above Earth's sea level. Up to 100 Kilo Meters, it is atmosphere of our Earth. The line between the atmosphere and space is known as Karman Line.
On 3rd October 1942, Nazi Germany launched its V2 Rocket, which was a military program. It was the first rocket to cross the Karman Line and enter the outer space.
V2 rocket was a long range Ballistic Missile. It was 14 Meters in length and 1.65 Meters in Diameter, weighing 12.5 Metric Tonnes. If launched vertically it could reach up to 206 Kilo Meters of height, more than the double distance of the Karman line.
After the end of World War II, United States, Soviet Union and British Government gained designs of this rocket, as well as the German scientists developing it. Thousands of the rockets were seized, and later were tested and modified.
Modern rocket technology is based on V2 rocket technology. So this rocket is knows as progenitor of modern rockets.
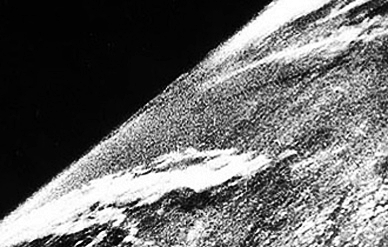
First Picture of Earth from Space: 10th October 1946
In a V2 Rocket Mission, USA took first photograph of Earth from Space, from 105 Kilo Meters above sea level. 1 photo was snapped every 3 Seconds. A special camera for taking photographs through space was developed by Clyday Holliday, an Engineer at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory.
The V2 Rocket Mission was an achievement not just for Rocket Science, but also for space photography.
Before this photograph, the highest point from which Earth was photographed, was 22 Kilo Meters above sea level, through Explorer II Balloon in 1935.
First Insects into Space: 20th February 1947
On 20th February 1947, USA sent fruit flies into the space through its V2 mission. Scientists wanted to observe effects of radiation at high altitude on the insects. The rocket crossed the Karman line within 3 minutes and reached to the height of 109 Kilo Meters above sea level. The fruit flies were recovered alive through a parachute.
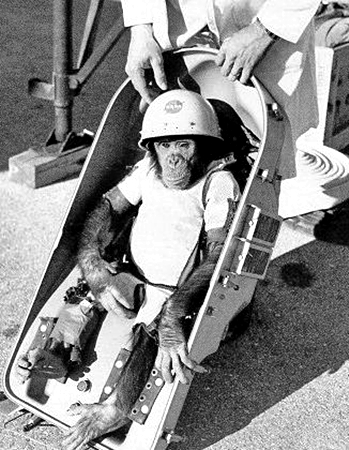
First Monkey into Space: 14th June 1949
On June 14th 1949, USA sent a monkey in space through V2 rocket. The rocket reached 134 Kilo Meters above sea level, passing the Karman Line.
It was a Rhesus monkey Albert II, the first primate to enter the space. The monkey died because of the parachute failure. Prior to this mission, another monkey Albert I was sent through another V2 mission which failed and could not reach to the space.
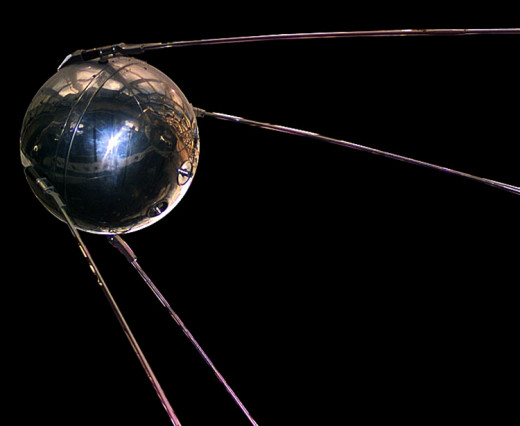
Sputnik1: First Artificial Satellite in Orbit: 4th October 1957
On 4th October 1957 Soviet Union (present day Russia) successfully sent an artificial satellite in the elliptical orbit. The satellite was Sputnik 1.
Sputnik 1 orbited earth for 3 months, took orbital period of about 100 Minutes per orbit, and completed 1440 orbits of the Earth. Its travel speed was 29000 Kilo Meters Per Hour. The satellite successfully sent radio signals from space which were monitored by amateur radio operators all over the world. The parameters of the elliptical orbit were: perigee height – 223 km, apogee height 1,450 km.
On 4th January 1958, Sputnik 1 fell from its orbit, entered the atmosphere of Earth and burned up. Before that, the satellite had completed 70 Million Kilo Meters of its travel.
The launch and success of Sputnik 1 was a shock for USA. It triggered space race between USA and Soviet Union.


Sputnik 2: First Animal in Orbit: 3rd November 1957
Sputnik 2 was second spacecraft to orbit Earth. It was sent to orbit on 3rd November 1957, with a living animal. The animal was a trained street dog, Laika. The spacecraft was quipped with advanced equipments like Temperature Control System, Radio Transmitters, Telemetry System and many other scientific instruments.
On day 6, Laika died as her Oxygen ran out.
Sputnik 2 completed 2000 orbits. It was in the orbit for 162 days, then entered the atmosphere of the Earth and was destroyed.
First Photograph of Earth from Orbit: 7th August 1959
On 7th August 1959, USA launched a small satellite, Explorer 6. It had a device for photographing the cloud cover of Earth. Explorer 6 successfully took and transmitted photographs of the Earth taken from the orbit.
First Spacecraft Lands on the Moon: 13th September 1959
Luna 2 of Soviet Union was the first spacecraft to reach the surface of the Moon. It was successfully impacted on the surface of the Moon on 13th September, 1959. It was a crash landing.
First Photographs of Far side of the Moon: 4th October 1959
Luna 3 was another Moon Mission of Soviet Union in 1959. This spacecraft took photographs of the other side of the moon, which we never can see from the Earth. Moon orbits Earth in about 27.5 days, and it takes the same time to orbit around itself. So we always see the same side of the Moon from Earth.
The spacecraft took total 29 photographs, from a distance of 63500 to 66700 Kilo Meters. The photographs were grainy, but they helped to create a tentative atlas of the other side of the moon.

First Animals to Return Alive from Orbit: 19th August 1960
Soviet Union sent two dogs, two rats, 40 mice and many plants to the orbit through its Korabl-Sputnik 2 (also known as Sputnik 5) satellite on 19th August 1960. All the animals were returned to the Earth safely after 3 orbits.
This was another great achievement in the history of space science.
The to dogs were Belka and Strelka. Strelka later gave birth to puppies. One of the puppies was sent to Jacqueline Kennedy, President John F Kennedy's wife as a present.

First Human Spaceflight: 12th April 1961
Vostok1 mission of Soviet Union was the first ever manned mission to space. This spacecraft took Yuri Gagarin to space on 12th April 1961. This was a short time mission, which took just 108 minutes to complete. It was just one orbit, but the mission was very important and was the foundation of sending man in the space.
After entering in the orbit, Yuri Gagarin reported, "The craft is operating normally. I can see Earth in the view port of the Vzor. Everything is proceeding as planned". This was first ever human vocie sent from the space.
First Venus Flyby: 14th December 1962
Mariner 2 was USA mission to probe Venus. It was first planetary flyby.
Mariner 2 passed within 35000 Kilo Meters of the planet on 14th December 1962. It collected a lot of data and sent to Earth.
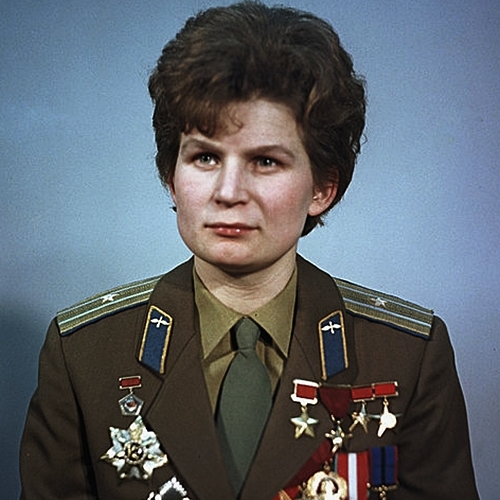

Valentina Tereshkova: First Woman in Space: 16th June 1963
Vostok-6 Mission of Soviet Union carried first woman astronaut into space on 16th June 1963. Her name was Valentina Tereshkova, and she was a civilian. So she was first civilian as well as the first woman to enter into space .
It was about 3 Days mission, and Valentina Tereshkova returned to Earth after 48 orbits.
First Mars Flyby: 14th July 1965
Mariner 4, a US spacecraft was launched to observe Mars, on 28th November 1964. The spacecraft reached as close as 9846 Kilo Meters to the Mars on 14th July 1965. It took first images of the surface of Mars and sent it to Earth.
First Soft Landing on the Moon: 3rd February 1966
Luna 9, a Russian Space Craft smoothly landed on the surface of the Moon on 3rd February 1966. It transmitted photographic data to the Earth.
First Landing on Venus: 1st March 1966
Venera 3 was a Soviet probe mission to Venus. The mission was to crash-land on the surface of Venus. Accordingly, it crash-landed on Venus on 1st March 1966. However, it failed to send any information as its communications system failed.
First Artificial Satellite Around the Moon: 3rd April 1966
Soviet Union launched Luna 10 spacecraft to orbit around the Moon. It entered Lunar orbit on 3rd April 1966. This spacecraft collected very important data about the Moon, including Moon's magnetic field, radiation belts and the nature of the rocks on the Moon.
First Manned Spacecraft to Orbit the Moon: 21st December 1968
Apollo 8 was the first manned spacecraft to orbit around the moon. It was the first successful mission to leave Earth orbit, to reach the Moon, to orbit it and to return safely to the Earth. A great achievement, which lead to land man on the moon within few months later.
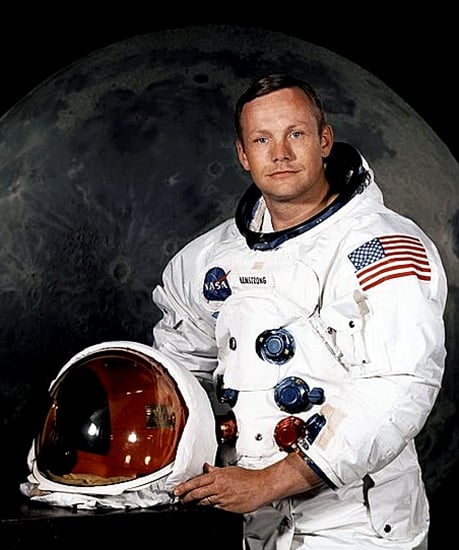

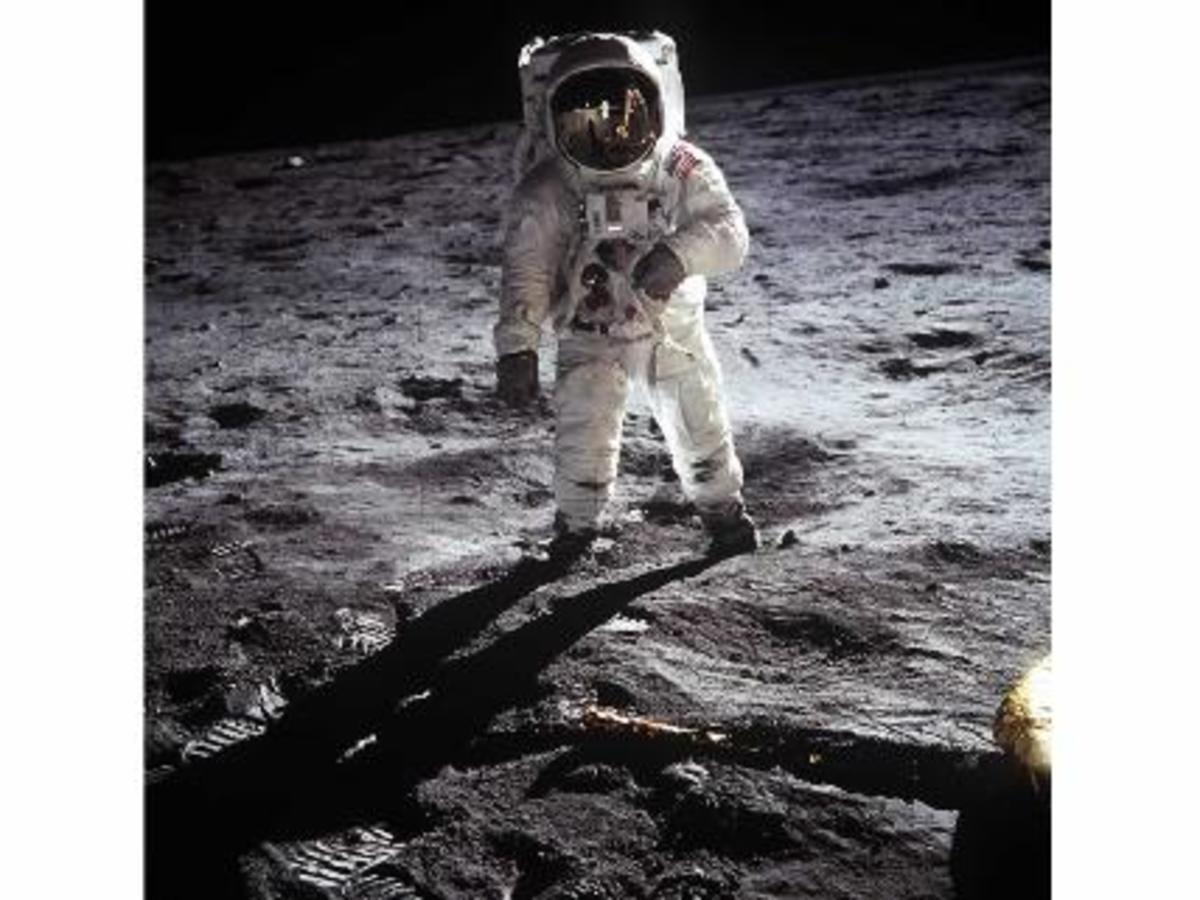
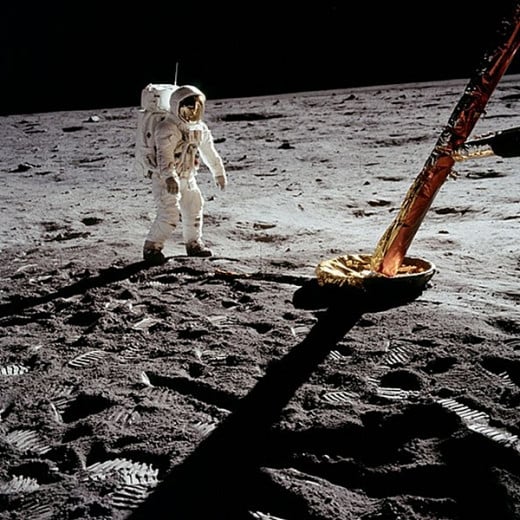
First Human Landing on the Moon: 20th July 1969
Finally, Man landed on the Moon. It was 20th July 1969. It was a great success of mankind, achieved within 28 years of first crossing the atmosphere of the Earth, and within 10 years of sending first man in the space.
Neil Armstrong was the first man to land on the Moon. It was Apollo 11 Mission of USA.
After landing on Moon, Neil Armstrong said, "This is one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind"
Please read my article about Neil Armstrong and his walk on Moon at: Neil Armstrong: The First Man to Walk on the Moon

Other Space Exploration Achievements
Besides above great achievements, there were many other important achievements in space exploration during 1942-1969.
1958: Explorer 1 of USA confirmed the existence of the Van Allen belts
1959: Luna 1 of Soviet Union First detected solar wind
1961: First Launch from orbit: Soviet Union's Venera 1 Mission
1963: First reusable crewed spacecraft: USA Mission X-15 Flight 90
1966: First orbital Docking between 2 spacecrafts: USA Mission: Gemini 8 and Agena target vehicle
1967: First crewless docking: Soviet Union Mission: Cosmos 186 and Cosmos 188
Astronomy Hubs
- Moon Landing Hoax: What is the Reality?
Many people believe that man never landed on the moon, and the said moon landing is just a hoax. What is the reality? - Do Aliens Exist?
Many people believe that Aliens visit our Earth regularly. They come through UFOs. But is it true or just a modern superstition? - Neil Armstrong: The First Man to Walk on the Moon
This is one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind -Neil Armstrong after landing on moon. It was the first quote from surface of moon. Neil Armstrong, the first man to walk on the moon, was my schooldays hero. I remember that I had pasted m - First Moon Landing: Apollo 11 Mission Postage Stamps
A collection of postage stamps on Apollo 11 Mission, issued by United States and other countries







